Get a Quote
How Does On-Grid Solar System Work at Night?
If you've recently installed or are considering installing a solar energy system for your home, you've probably wondered: How does an on-grid solar system work at night? This is a common question for homeowners who want to understand how they'll power their homes when the sun isn't shining. Let's break down how an on-grid solar system operates during the day and night, how it interacts with the public electricity grid, and the role that battery storage can play.
What Is an On-Grid Solar System?
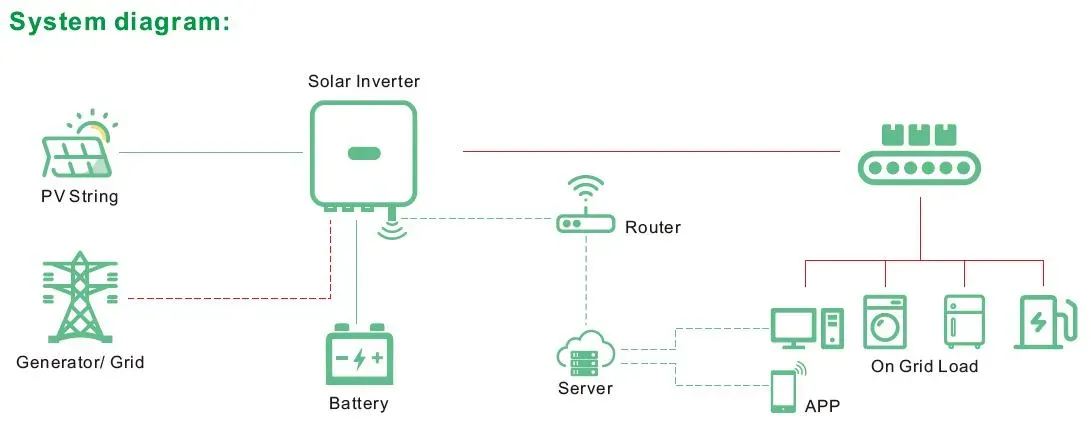
An on-grid solar system, also called a grid-tied solar system, is directly connected to the public electricity grid. During the day, your solar panels generate electricity using sunlight. Any excess energy that your home doesn't use gets sent back to the grid, and in return, you may receive credits on your electric bill through a process known as net metering.
But what happens when the sun goes down, and your solar panels can no longer generate electricity? That's where the grid connection becomes essential. Let's dive into how the system operates when there's no sunlight.
How Does an On-Grid Solar System Work at Night?
Simply put, solar panels do not generate electricity at night because there's no sunlight for them to convert into power. However, this doesn't mean that your home is left in the dark. Here's how your on-grid system functions after sunset:
Electricity from the Grid: When your solar panels stop generating electricity in the evening, your home automatically switches to drawing power from the grid. This ensures you have a continuous electricity supply without any interruptions.
Net Metering Credits: If your solar system generated excess electricity during the day, those extra kilowatt-hours (kWh) are sent back to the grid, and you earn net metering credits. At night, when you use electricity from the grid, these credits are applied to your usage, reducing or even eliminating your electric bill.
Smooth Transition: The switch from solar power to grid power happens seamlessly. You won't notice any change in the electricity supply, and the system handles it automatically.
What Is Net Metering, and How Does It Help at Night?
Net metering is a billing mechanism that allows homeowners with solar panels to send their excess electricity back to the grid and receive credits on their utility bill. This is one of the key reasons why on-grid solar systems are so efficient, even at night.
For example, if your solar system produces more energy than your home uses during the day, that extra energy is sent to the grid. Let's say your system generated 20 kWh of electricity, but your home only used 15 kWh. The remaining 5 kWh is credited to your account. At night, when your solar panels aren’t producing electricity, you can draw from the grid without being charged for those 5 kWh, thanks to your net metering credits.
This system ensures that you're maximizing your solar energy usage and minimizing your energy costs.
Can You Store Solar Energy for Use at Night?
While on-grid systems typically rely on the grid for power at night, many homeowners choose to add solar batteries to their system to store excess energy for later use. This is especially useful if you want to reduce your reliance on the public grid or if you live in an area prone to power outages.
How Solar Batteries Work:
- During the day, your solar panels produce electricity. If you generate more electricity than you need, the extra energy is stored in your solar battery.
- At night, instead of drawing power from the grid, your home can use the stored energy from the battery.
- If your battery runs out of power, the system will automatically switch to drawing electricity from the grid.
Key Benefit: With a battery storage system, you can use solar energy 24/7 and reduce your dependency on the grid, which is ideal for homeowners who want greater energy independence.
Let's say you install a solar battery for off-grid use at night. During a sunny day, your solar panels generate enough electricity to power your home and fill up your battery. When the sun sets, the battery takes over and powers your home during the night, allowing you to avoid grid electricity altogether.
Common Misconceptions About On-Grid Solar Systems at Night
There are several misconceptions surrounding how on-grid solar systems work at night. Let's clear up a few:
Myth: Solar panels generate power at night.
- Reality: Solar panels need sunlight to generate electricity, so they don't produce power at night. However, on-grid systems ensure your home has electricity by pulling from the public grid.
Myth: You need a battery to use solar energy at night.
- Reality: You don't necessarily need a battery if you're connected to the grid. You can rely on the grid for nighttime power and still reduce your overall electricity costs through net metering.
Myth: Solar panels are useless if the sun isn't shining.
- Reality: Even though solar panels don't generate electricity at night, an on-grid system allows you to benefit from solar energy during the day and access grid power at night, providing continuous power.
How On-Grid Solar Systems Compare to Off-Grid Systems at Night?
If you're curious about the pros and cons of on-grid and off-grid solar systems, it's important to note how these systems differ in handling nighttime power.
On-Grid Systems: As we've explained, on-grid systems rely on the public grid when the sun isn't shining. This means you don't need to worry about running out of power at night, as the grid provides backup.
Off-Grid Systems: Off-grid systems are entirely independent of the public grid and require solar batteries or a backup generator to provide power during the night. While this offers complete energy independence, it also comes with higher costs and the need for larger battery storage.
Innovative Solutions for Solar Energy at Night
With technological advancements, solar energy is becoming more efficient and adaptable. If you’re using an on-grid system, there are several innovative technologies that can maximize the benefits of your solar setup, even during the night. Let's explore some of these emerging solutions:
Solar Energy Storage with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- How It Works: AI-powered energy management systems can optimize the use of stored solar energy. These systems analyze your household's energy consumption patterns, weather forecasts, and energy pricing trends to determine when to use stored energy or draw power from the grid.
- Benefits: Homeowners using AI-driven systems can reduce their reliance on the grid at night by efficiently managing stored solar energy and reducing overall energy costs.
Grid-Connected Solar with Demand Response
- How It Works: In demand response programs, utilities incentivize homeowners to reduce electricity use during peak hours. This allows homeowners to manage their energy consumption smartly by using stored solar energy or reducing unnecessary energy usage at night when grid demand is high.
- Benefits: Participating in demand response programs can lower your energy costs, especially if you use solar batteries to cover your nighttime energy needs when electricity is most expensive.
Hybrid Solar Systems with Advanced Inverters
- How It Works: Hybrid solar systems combine the benefits of on-grid and off-grid systems, allowing homeowners to store excess solar energy while staying connected to the grid. These systems use advanced inverters that automatically switch between solar, battery, and grid power depending on demand.
- Benefits: Hybrid systems provide more flexibility, allowing you to store solar power for nighttime use while still drawing from the grid when necessary. This reduces your reliance on the grid without the need for full off-grid independence.
Smart Solar Panels with Integrated Tracking Systems
- How It Works: Some modern solar panels come with tracking systems that adjust the angle of the panels throughout the day to capture more sunlight. These systems can increase efficiency by up to 30%, ensuring you generate the maximum amount of electricity during the day to store for use at night.
- Benefits: By generating more electricity during the day, you can increase the amount of energy stored in batteries, reducing the need to rely on the grid during the night.
Conclusion: How Does On-Grid Solar System Work at Night?
To sum it up, on-grid solar systems work seamlessly at night by relying on the public electricity grid. While your solar panels don't generate electricity without sunlight, the grid provides a reliable backup, and with net metering, you can minimize your energy costs by using credits from excess daytime energy production.
If you're looking for more independence from the grid, you can add solar batteries to store excess energy during the day for use at night. This setup provides flexibility and allows you to use solar energy 24/7.
FAQs
1. Do I need a battery for my on-grid solar system to work at night?
No, you don't need a battery. Your home will automatically draw power from the public grid at night.
2. Can I go completely off-grid with a solar system?
Yes, but you'll need sufficient battery storage or a backup generator to ensure you have power at night or during cloudy days.
3. How does net metering help reduce energy costs?
Net metering allows you to earn credits for excess energy sent to the grid, which can be used to offset your electricity consumption at night.